Hexagon nuts, screws, and bolts are used in conjunction with each other to connect and tighten mecha...
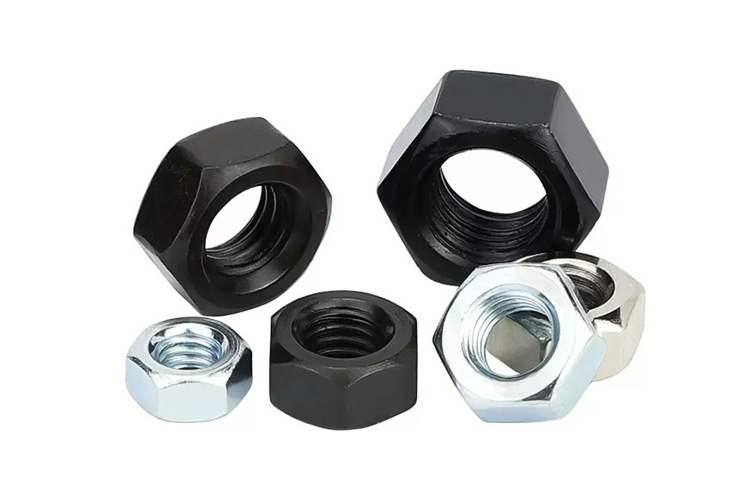
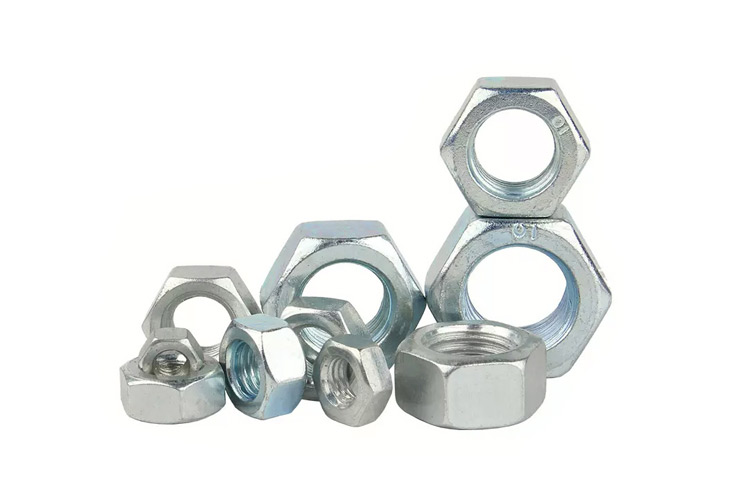
View moreHexagon nuts, screws, and bolts are used in conjunction with each other to connect and tighten mechanical components. Among them, Type 1 six purpose nuts are the most widely used, while C-grade nuts are used on machines, equipment, or structures with relatively rough surfaces and low precision requirements; A-grade and B-grade nuts are used on machines, equipment, or structures with relatively smooth surfaces and high precision requirements. The thickness M of type 2 hex nuts is relatively thick and is often used in situations where assembly and disassembly are frequently required. The thickness M of Hexagon thin nuts is relatively thin and is often used in situations where the surface space of the connected parts is limited.
Hexagon nuts are classified into three types based on their nominal thickness: Type I, Type II, and Thin. Nuts above level 8 are divided into two types: Type 1 and Type II. Type I hex nuts are the most widely used, and Type 1 nuts are divided into three levels: A, B, and C. Grade A and B nuts are suitable for machines, equipment, and structures with low surface roughness and high precision requirements, while Grade C nuts are used for machines, equipment, or structures with relatively rough surfaces and low precision requirements; The thickness of type 2 hex nuts is relatively thick and is often used in situations where assembly and disassembly are required.
Type 1 nut refers to a regular Hexagon nut with a nominal height m ≥ 0.8D, and its type and size should comply with the provisions of GB/T6170; The height of type 2 nuts is higher than that of type 1 nuts, and their type and size should comply with GB/T6175. The purpose of adding type 2 nuts is twofold: firstly, to obtain a cost-effective nut that does not require heat treatment by increasing the height of the nut. Because grade 8 type 1 nuts with D ≤ M16 do not require heat treatment, only grade 2 nuts are used for sizes D>M16-39 in grade 8 nuts. Obviously, type 1 nuts that do not require heat treatment cannot meet the mechanical performance requirements of grade 9 nuts. Another purpose of specifying Type 2 nuts is to obtain Grade 12 nuts with better toughness. Due to the increased height of the nut, the guaranteed stress index can be achieved at lower quenching and tempering hardness, thus increasing the toughness of the nut. Classified by tooth spacing: standard teeth, regular teeth, fine teeth, extremely fine teeth, and reverse teeth. Classified by material: stainless steel hex nut, carbon steel hex nut, copper hex nut, iron hex nut. Classified by thickness: Hexagon thick nuts and Hexagon thin nuts. Classified by usage: Hot melt copper nuts, hot pressed copper nuts, embedded copper nuts, and ultrasonic copper nuts.